Institute of Pharmacology and Toxicology
Research and diagnostic services
The Institute of Pharmacology and Toxicology offers the following methods and analyses as part of diagnostic service and scientific collaboration projects for academic institutions and companies:
State of the art patch-clamp set-up composed of an EPC 10 USB amplifier (HEKA, Germany), pneumatic anti-vibrating table, piezoelectric micromanipulator (Scientifica), inverted phase contrast microscope (Motic AE31) equipped with epi-fluorescence and FITC and TRITC emission filters for identification of transfected cells, perfusion system with ALA VC4 valve commander and vacuum pump, Macintosh computer running the PatchMaster acquisition software. Users will have access to a horizontal puller (Sutter Instruments) and a microforge (Narishige) for construction of electrodes and to a biosafety level II cell culture room.
The electrophysiology facility is part of COMPCEL. Please find more information about COMPCEL (Competence Center for Electrophysiology) here.
This ABR Workstation can record auditory brainstem activity (ABR), which reflects the function of cochlear and retrocochlear pathways, as well as distortion-product otoacoustic emissions (DPOAE), which specifically reflect the activity of cochlear outer hair cells of the organ of Corti. In addition, the system is configured to acquire evoked responses from any region of the brain using scalp electrodes or implanted skull electrodes following stimulation of various sorts. The system easily controls third-party external devices such as mini shakers (vibration equipment), light sources such as LEDs, and thermoelectrical devices. Additional components and software allow the system to acquire spiking activity from individual neurons or control systems for behavioral neuroscience.
The ABR Workstation is from Tucker-Davis Technologies (TDT), which has been in the business of signal processing and auditory neuroscience for over 30 years and is unanimously recognized as the best provider of auditory research devices by experts in the field, and is located within the conventional area of the animal facility at PMU Salzburg.
The ABR Workstation is part of COMPCEL. Please find more information about COMPCEL (Competence Center for Electrophysiology) here.
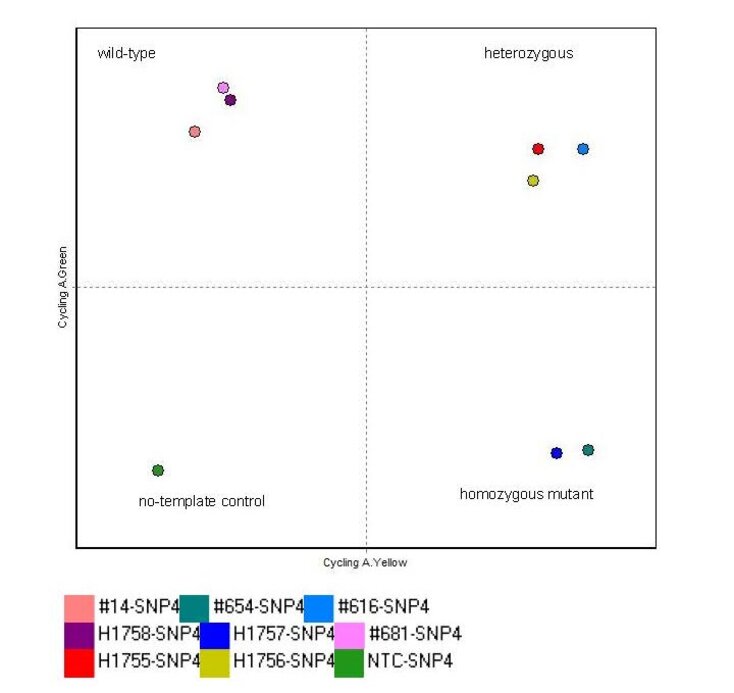
Single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) assays determine prevalence and genotype one or more SNPs in a given cohort. Genomic DNA is extracted from no more than 350 ul of peripheral blood using the automated EZ1 Advanced XL platform (Qiagen) and subjected to real-time PCR with allele-specific primers and a probe-based reporter system on a Rotor Gene Q instrument (QIAGEN), which can run 72 samples simultaneously.
The Institute of Pharmacology and Toxicology holds the approval for diagnostic gene analysis issued by the Bundesministerium für Arbeit, Soziales, Gesundheit und Konsumentenschutz, Austria (approval number: BMASGK-76120/0007-IX/B/16c/2018). The genes analyzed are GJB2, GJB6, SLC26A4 and POU3F4, all of which play a fundamental role in determining sensorineural hearing loss associated with malformations of the inner ear. Additional genes are analysed for research purposes.
Localization of a protein within a given subcellular compartment or co-localization of two or more proteins within a cell are useful strategies to unravel protein function, interaction, and trafficking. Co-localization of native or recombinant proteins in living or fixed cells is quantified and statistically analyzed to disclose differences between protein variants or different conditions. Markers of cellular compartments, including nucleus, plasma membrane, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi complex, mitochondria, and autophagosomes permit the identification of the specific subcellular compartment of a protein. Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET) permits the identification and characterization of direct interactions beween protein pairs in living or fixed cells in various experimental conditions. Molecular imaging is performed with a Leica TCS SP5 II confocal microscope equipped with 4 lasers and 8 excitation wavelengths (405, 458, 476, 488, 496, 514, 561, 633 nm).
State of the art true confocal system, equipped with 4 lasers (Diode, Argon, DPSS, Helium/Neon) giving 8 excitation lines (405, 458, 476, 488, 496, 514, 561, 633 nm), conventional and resonant scanner for fast acquisition speed, acousto-optical beam splitter (AOBS) for better transmission of the emitted light, acousto-optical tunable filter (AOTF) for fine control of laser power, 3 photomultipliers (PMTs) with spectral detectors for free choice of the emission window and one hybrid detector (hyD) for optimal signal-to-noise ratio acquisition in the red emission region, 5 objectives (10x, 20x, 40x and two 63x) including one 63x water immersion objective for imaging of living samples, temperature, humidity and CO2 control. The confocal microscope is housed in a biosafety level II laboratory room equipped with one biosafety level II hood, one cell culture incubator, fridge, freezer, one small fume hood, one system producing type III deionized water.