New Insights into Achilles Tendinopathy: International Study Highlights Causes and Innovative Therapeutic Approaches

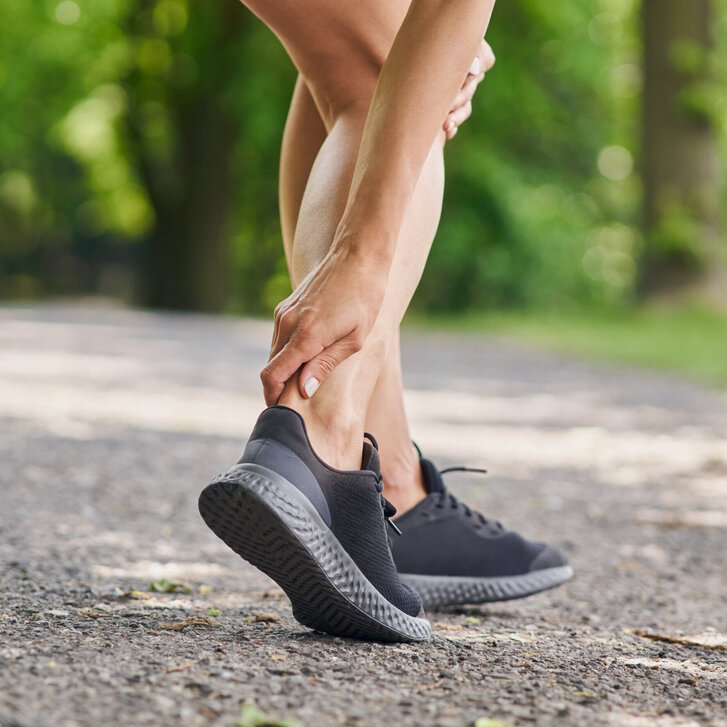
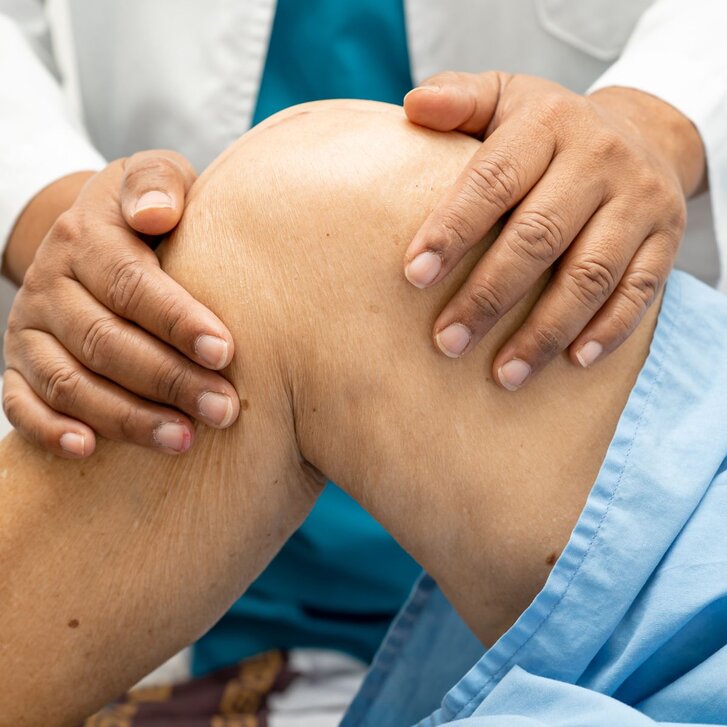
The Achilles tendon is one of the most frequently injured tendons in the human body. Achilles tendinopathies (AT) affect up to 6% of the general population and up to 50% of all elite athletes. Typical symptoms of AT include pain, limited function, and often a palpable swelling of the tendon—usually due to chronic overuse. However, the condition is multifactorial: aging processes, genetic predisposition, biomechanical influences, and cellular dysfunctions play a central role. Many affected individuals suffer from chronic symptoms for years, which are often associated with reduced physical capacity and long-term functional impairments.
Despite intensive research, there is still no treatment method available that ensures complete structural and functional regeneration of the Achilles tendon comprehensively and permanently. Therefore, the treatment of AT remains a lengthy and challenging task—both for those affected and for medical professionals. An international research group, including Andreas Traweger from the Institute for Tendon and Bone Regeneration at the Paracelsus Medical University (PMU), has intensively studied the underlying mechanisms of the disease. Their findings, published in Nature Reviews Disease Primers, provide comprehensive insights into the biological basis of AT and promising new therapeutic approaches.
The current research focuses on optimizing treatment strategies—whether through more targeted rehabilitation measures or the use of innovative methods such as regenerative medical products. The goal is to increase therapeutic efficacy and improve patients' quality of life in the long term.
Learn more at Nature Reviews Disease Primers.
Translated by Le Chat / Mistral AI